The Importance of Internal Linking for Blog Traffic Growth
When people think about SEO, they usually rush to talk about keywords, backlinks, or site speed. But what often flies under the radar is internal linking — a powerful, often-overlooked strategy that quietly drives traffic, improves user experience, and helps your blog grow at scale.
Internal links are more than just tools for site navigation; they help search engines understand your content structure and guide readers to relevant pages, improving visibility and engagement. If you’ve been pouring hours into writing blogs and still not seeing the traffic move the way you want, there’s a high chance you’re missing out on internal linking.
A 2024 study by FirstPageSage ranks internal linking among the top five on-page SEO factors, alongside content quality and mobile optimization.
So no, it’s not just a quick fix — it’s a habit. And it’s one of the most sustainable, high-impact practices you can build into your content strategy. Read this blog till last and learn more about how internal linking improves blog traffic growth.
What is Internal Linking?
Internal linking means connecting one page on your website to another page on the same domain. It can be a link from one blog to another, from a product page to a buying guide, or from your homepage to a contact page.
Here’s how it’s different from external links:
- Internal links stay within your website.
- External links point to other websites.
For SEO, internal linking is like handing Google a map of your site. It shows what pages on your site matter, how they relate, and which ones deserve more visibility. One of the key benefits of interlinking is that it gives users a smoother reading experience — no dead ends, just value at every click.
Types of Internal Links
Understanding the different types of internal links is essential to building a strong blog SEO strategy. Each type serves a unique function in helping both users and search engines navigate your website efficiently.
Here’s a breakdown of the most commonly used internal links:
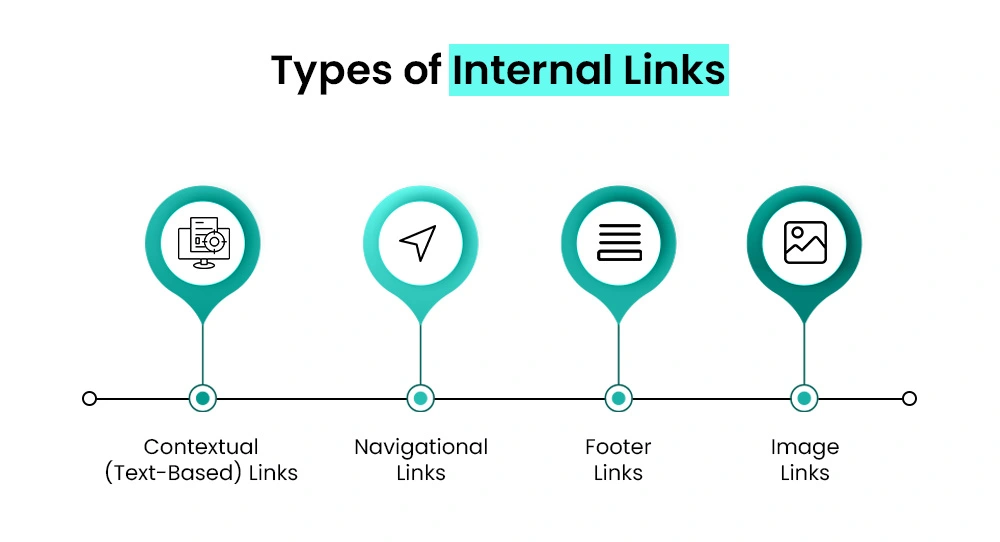
1. Contextual (Text-Based) Links
These are hyperlinks placed within the body of your content. A text link points to other relevant pages within your website, such as related blog posts, product categories, or resources.
They are crucial for passing link equity, enhancing user experience, and reinforcing topical relevance. Contextual links are central to effective SEO internal linking because they signal to search engines what content is most valuable.
2. Navigational Links
Typically found in site menus, sidebars, or headers, these links help users explore the primary sections of your website. Strong navigational structures ensure that essential pages are easily accessible, which improves site architecture and crawlability. These links also support SEO internal linking best practices by guiding both visitors and search engines to cornerstone content.
3. Footer Links
Footer links usually lead to static pages like Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy, or About Us. However, when used wisely, they can also drive traffic to underutilized but important pages. While they may hold less SEO weight than contextual links, they still contribute to a comprehensive HTML internal link architecture.
4. Image Links
Linking through images isn’t very common, but it can still work well when done right. Just make sure the image has clear, descriptive alt text; this helps with accessibility and image SEO.
Using different types of internal links—like image links, text links, or even basic HTML internal link formats—helps build a stronger, more organized website. Whether it’s a blog, an online store, or a company site, smart internal linking makes it easier for both people and search engines to move around your content.
If you’ve been wondering:
- How to find internal links to a page
- How many internal links per page does SEO allow for best performance
- Internal link analysis for landing pages
… checking these regularly can help you spot areas to improve and build a better visitor experience.
How Internal Linking Supports Blog Traffic Growth
Internal linking plays a big role in growing your blog’s traffic. It does more than just connecting your content—it helps both users and search engine crawlers better understand your website.
1. Facilitates Search Engine Crawling and Indexing
Think of internal links as road signs for search engines like Google. These bots crawl your site by following links pointing from one web page to another.
When your site’s pages are linked properly, search engines find and understand them more easily.
For example, if you write a new blog post and add internal links to it from your homepage or a popular article, Google will discover it faster.
This improves your chances of getting indexed quickly and appearing in search results sooner.

The more internal links point to a page, the easier it becomes for search engines to discover, crawl, and index it effectively.
2. Enhances User Navigation and On-Page Experience
Internal links provide clear navigational paths for users and signal to search engines how your content is structured, improving user experience and crawlability.
If someone reads a blog post about SEO basics, and you add internal links to another article on keyword research, you’re helping them explore related content. This makes the experience smoother and more useful.
Good navigation keeps people from getting stuck or confused. It creates a natural flow from one topic to the next.
When visitors can easily find what they need, they’re more likely to trust your brand and come back for more. That trust often turns into leads, sign-ups, or even sales.
3. Increases Session Duration and Lowers Bounce Rate
Want people to stay longer on your site? Internal links help with that, too.
Adding internal links within your content encourages deeper user engagement, which increases session duration, a key behavioral signal that can positively influence search engine rankings.
It also reduces the number of people who leave after visiting just one web page (known as the bounce rate).
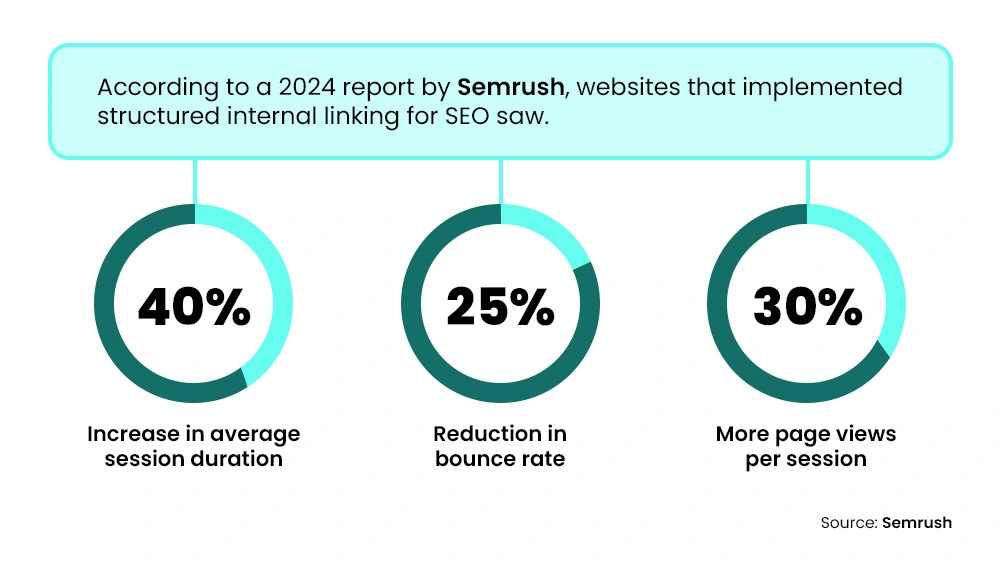
Search engines look at both of these metrics when ranking your site. A longer session and a lower bounce rate tell Google that your content is valuable and engaging.
So, every well-placed internal link can directly improve your site’s SEO performance.
4. Distributes Link Equity Across Pages
Not every page on your website has the same SEO power. Some pages, like your most visited blog posts, carry more authority.
With internal linking, you can share that authority with other important pages.
For instance, if your top-performing post links point to a newer or less-visited post, that “link equity” gets passed along.
This helps boost rankings for pages that might otherwise struggle to be seen.
SEO internal linking doesn’t just help your readers—it strengthens your entire SEO foundation. When used wisely, it can directly impact how well your content ranks in search engines.
Internal Linking and SEO Performance
Internal linking plays a vital role in shaping how search engines interpret your website and how users experience your content. It’s not just a structural tactic—it’s a core SEO strategy that helps improve visibility, authority, and long-term performance.
Let’s explore how it supports your site’s SEO success:
Boosting Topical Relevance and Contextual Authority
Strategic internal linking for SEO allows you to connect related pages within your site, reinforcing subject matter depth. For instance, if you’ve published multiple articles on SEO techniques, linking them together helps create a topic cluster. This approach signals to search engines that your content offers comprehensive coverage of the subject, enhancing both topical relevance and contextual authority.
Over time, this structure strengthens your ability to rank for related search terms. It also improves the user journey by guiding readers toward logically related information, reducing bounce rates, and increasing session duration.
Incorporating internal linking best practices into your strategy, such as anchor text optimization and ensuring each key page receives sufficient links, creates a clear content hierarchy. This not only helps users but also informs search engines of your most important pages.
Helping Search Engines Understand Site Structure
SEO internal links help search engine crawlers navigate your site structure effectively. They provide clear pathways between pages on your site, showing how your content is organized and how different topics relate to each other.
A well-planned internal linking structure highlights which pages on your site are the most important. For instance, if multiple blog posts link back to your main “SEO services” web page, search engines will treat that page as a key resource.
This structure helps Google and other search engines understand your content hierarchy. As a result, it improves the chances of more of your content being indexed and ranked appropriately.
Without internal links, even high-quality pages may remain hidden from search engines if they’re not easily discoverable.
Reviving and Supporting Underperforming Content
Not all content on your website performs well from the beginning. Some pages may have value but fail to attract traffic over time.
Internal linking gives these pages another chance.
By adding internal links from popular or high-traffic pages to underperforming ones, you direct both users and search engines toward content on your website that might otherwise go unnoticed.
This can increase web page views, improve engagement metrics, and even lead to better rankings as search engines reassess the relevance of the linked content.
It’s a cost-effective way to boost SEO performance—without the need to create new content.
Building a Strategic Internal Linking Structure
Internal linking is more than just connecting one page on your website to another. When done right, it becomes a powerful part of your blog SEO strategy and enhances the overall user experience. A well-planned internal linking structure helps search engines understand your site’s structure and guides users toward the most valuable and relevant content.
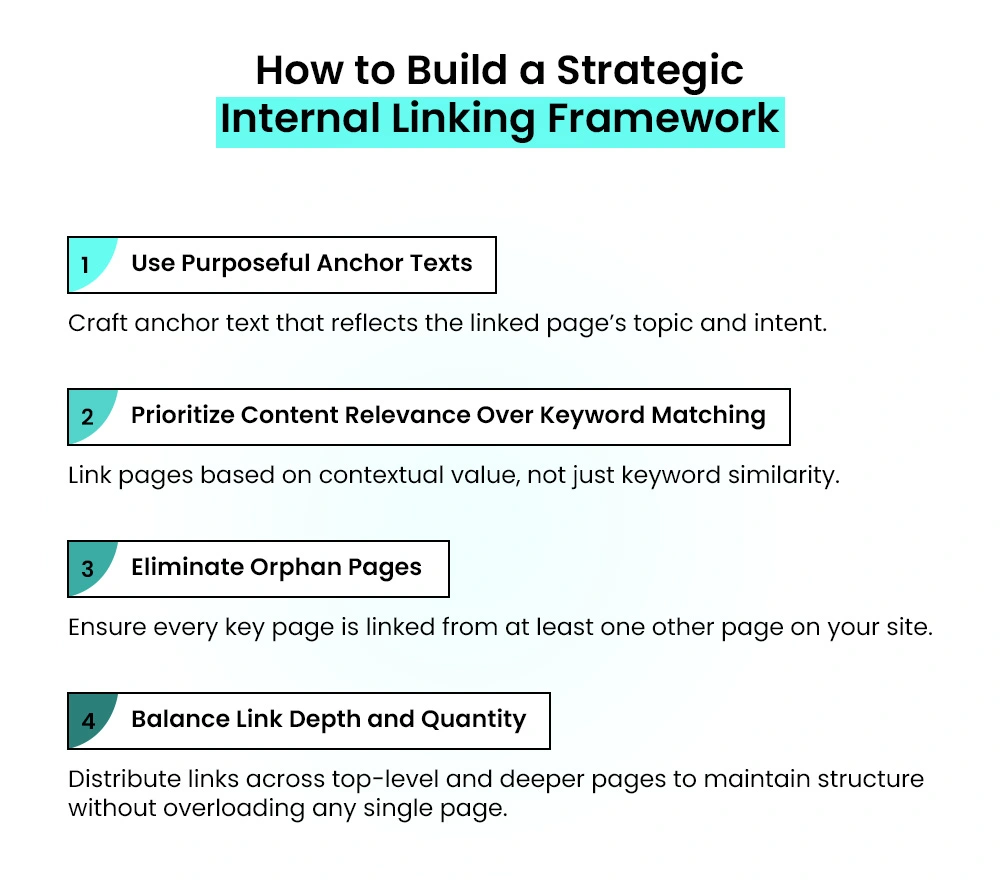
Choosing the Right Anchor Texts
Anchor text—the clickable part of the link—matters more than most people think.
Search engines use anchor text as a clue to determine what the linked web page is about. If you use vague terms like “click here” or “read more”, you’re missing a key opportunity to pass context and relevance. Instead, anchor texts should clearly describe what the user will find if they click.
For example, linking to a page on your website using the phrase “descriptive anchor text on-page SEO checklist” gives both users and search engines clarity.
Your anchor text should be:
- Descriptive anchor text yet concise – No need for long phrases, but don’t be too generic either.
- Relevant to the destination web page – It should match what the user will see after clicking.
- Naturally varied – Don’t use the same phrase every time; mix it up with synonyms and variations.
Avoid stuffing the same keywords into every link. Over-optimization looks unnatural and can harm your SEO. Anchor text should sound like something a real person would write and click on.
Linking Relevant Content, Not Just Keywords
Think about what the user is trying to learn, do, or solve. Is the linked web page going to help them move forward? If not, skip the link.
For example, someone reading a post on technical SEO is probably already familiar with basic SEO concepts. Linking them to a “what is SEO” guide doesn’t add value. But a link to core web vitals, structured data, or JavaScript SEO? That’s much more aligned with their intent.
Internal linking guides your readers to deeper, more relevant resources, not just checking off a keyword box.
Avoiding Orphan Pages
Orphan pages are like forgotten corners of your website. These are pages that have no internal links pointing to them.
When a page lacks internal links, search engines may not index it properly, reducing its visibility to both crawlers and users. That’s a major missed opportunity, especially if the content on your website is valuable.
To fix this,
- Run regular site audits using tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to identify orphaned pages.
- Locate relevant spots within your existing content to add internal links to those pages.
- Ensure every important page is linked from at least one other page—ideally multiple pages—for better discoverability.
A well-connected web page is easier to crawl, easier to rank, and more likely to engage your readers.
Balancing Depth and Link Quantity
Internal linking is good, but moderation is key.
Linking to every possible related article in one post doesn’t help your readers. Too many links can feel overwhelming and confusing. Plus, they dilute the SEO value each link passes.
On the flip side, having too few links can isolate content, making it hard for users and search engines to explore your site.
Here’s how to keep things balanced:
- Link only where it adds real value.
- Spread links naturally throughout your content on your website—not all in one spot.
- Focus on quality, not quantity.
- Aim to create a smooth reading experience. Internal links should feel like helpful suggestions, not distractions.
Tools and Techniques to Audit and Optimize Internal Links
Even the best internal linking structure won’t last if you don’t maintain it. As your site grows and changes, you need to keep an eye on how your links are working.
How to Find Internal Links Pointing to a Page on Your Website
To improve internal linking, you first need to know where your current links are. This helps you identify which pages on your site are well-supported and which ones are being ignored.
Here are some easy ways to check:

With these insights, you can decide where to add internal links and which links may need adjustments.
Recommended Internal Linking Tools
The right tools make managing internal links much easier and faster.
- Screaming Frog: A must-have crawler for auditing your website. It detects broken links, orphaned pages, and duplicate anchor text patterns.
- Ahrefs: Offers clear internal link reports, showing how link equity flows through your site and highlighting areas to improve.
- Yoast SEO (for WordPress): Suggests internal links while you write and keeps track of pages with few or no incoming links.
These tools save time and help you build a stronger, cleaner link structure.
Fixing Broken or Irrelevant Links
Broken internal links are bad news for both SEO and user experience. They create dead ends, frustrate visitors, and waste crawl resources for search engine crawlers.
That’s why regular link audits are essential. At least once every quarter, run a full crawl of your site using a tool like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs. Look for:
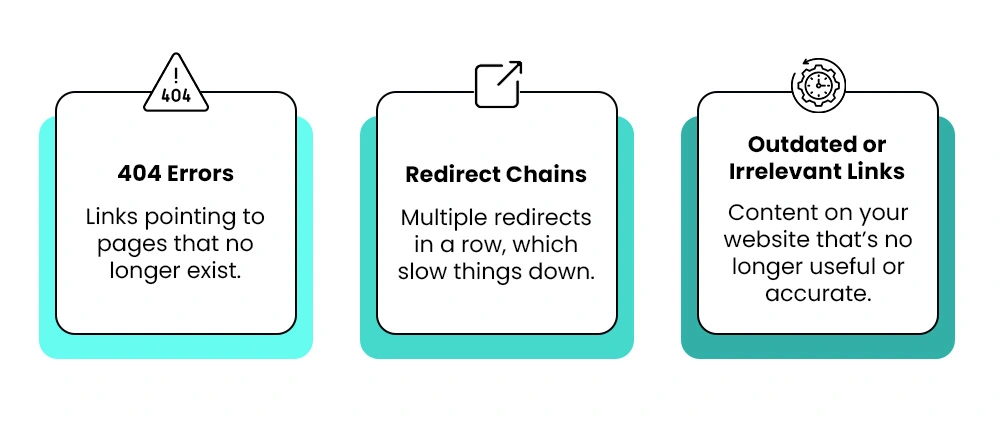
Fix broken links by replacing them with the accurate and current URLs. If the target web page is gone, either replace it with a similar resource or remove the link. When a page on your website has moved, use a proper 301 redirect.
Maintaining clean and relevant internal links improves usability, boosts search engine trust, and reflects positively on your brand.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Internal linking seems simple. But small mistakes can create big problems for both users and search engines. Here are some frequent mistakes and tips on how to prevent them.
How Many Internal Links Per Web Page SEO Standards Suggest
- Google doesn’t penalize for having “too many” links, but filling 100+ links into a web page can overwhelm readers and dilute SEO value.
- Aim for 5–15 meaningful internal links per 1,000 words.
- Focus on relevance and flow, not just numbers.
- Only add internal links where they help users go deeper into a topic.
For example, a blog on “SEO for beginners” can add internal links to related guides like “Keyword Research Basics” or “Technical SEO Checklist.” But avoid linking just because it includes the word “SEO.”
Each link should feel natural and useful. Not forced.
Avoiding Link Cannibalization and Over-Optimization
Link cannibalization occurs when multiple pages target the same keyword, each linked with identical or very similar anchor text. This creates confusion for both users and search engines.
Why?
Because Google can’t tell which web page is the main authority on that topic. You’re splitting your SEO power, and that weakens all the pages on your site.
Example of Link Cannibalization:
Let’s say you have three different blog posts:
- “Beginner’s Guide to Keyword Research”
- “Advanced Keyword Research Techniques”
- “Free Keyword Tools for SEO”
Now, if you keep adding internal links to all three pages using the anchor text “keyword research guide”, Google won’t know which one is most relevant for that phrase. You’re competing against yourself.
Instead, choose one important page to rank for that main term (e.g., the beginner’s guide). Links point to it using anchor texts like:
- keyword research guide
- Learn keyword research
- How to do keyword research
Then, use more specific anchor texts for the other pages, like:
- Advanced keyword tips
- Best free keyword tools
This way, each page supports the overall topic, but they don’t compete against one another.
Keeping Links Updated with Content on Your Website Changes
Internal links aren’t “set and forget.” As your site evolves, some pages on your site disappear. Others get moved. Content on your website gets updated. If your links don’t keep up, you risk:
- Broken links (404 errors)
- Redirect chains
- Outdated resources
- Frustrated users
Here’s how to stay on top of it:
- Run a quarterly internal link audit with tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs.
- Check for any broken or redirected links.
- Update the anchor text if the destination has changed focus.
- Replace links to deleted content with fresh, relevant alternatives.
Your internal linking structure should evolve as your website grows. Don’t let old links drag you down.
Conclusion
A strong internal linking strategy isn’t about shortcuts—it’s about serving your users first. When done right, internal links help readers explore, understand, and trust your content on your website.
One of the key benefits of interlinking is that it also makes it easier for search engines to crawl and rank your pages more effectively.
At Mastroke, we understand that SEO and internal linking can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. Our team is here to help you create a smart, structured linking strategy that not only improves your search rankings but also keeps your users engaged.
Whether you’re just getting started or looking to refine your existing SEO approach, we’re ready to guide you every step of the way. Let’s build better SEO together—connect with us today.
FAQs
1. What is internal linking in SEO, and why is it important?
Internal linking refers to linking one page of a website to another within the same domain. It helps search engines crawl your site more efficiently and improves user navigation, enhancing SEO performance.
2. How many internal links should I include on a page?
There’s no fixed number, but focus on relevance and user experience. Generally, 3–5 internal links per 1,000 words is a safe guideline. Avoid overstuffing or forcing links unnaturally.
3. Do internal links help with keyword rankings?
Yes! Strategic internal linking helps distribute page authority and can boost keyword rankings for linked pages, especially when anchor texts are optimized.
4. What’s the difference between internal and external links?
Internal links connect pages within your site, while external links point to other websites. Both are important—internal links structure your site, and external links build credibility.